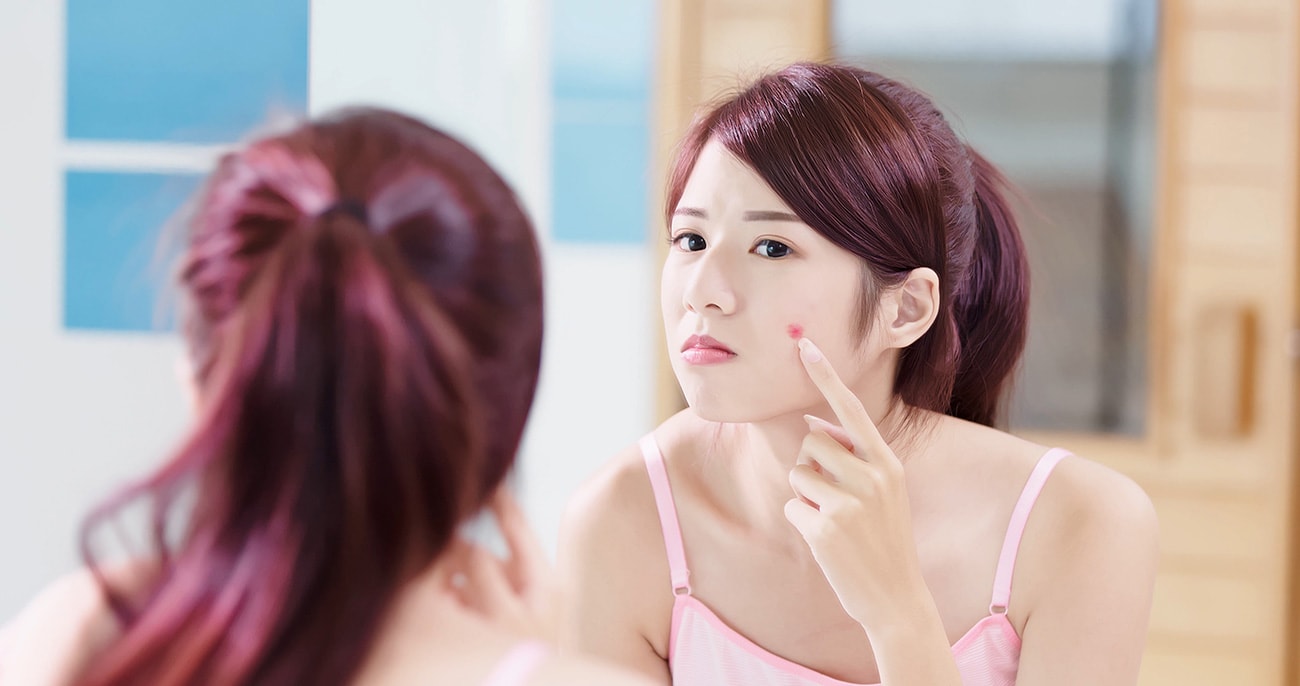
Acne is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease. 85 per cent of people suffer from acne. Acne presents as spots or pimples on face, neck, chest, shoulders, back, upper arms and buttocks. The major problem of acne is that it is disfiguring and leaves scars which are permanently disfiguring and affect the psyche.
The Different Types Of Acne
Acne can be classified by appearance (whitehead, blackhead, nodule, cyst), location (face, chest, back, buttock) and severity (mild, moderate, severe)
Whiteheads: Acne remains under the skin and appears white or yellowish small bumps
Blackheads: Appear like whiteheads but instead of a white bump, they appear as black spots
Papules: Red inflamed bumps caused when a pore or hair follicle becomes blocked and gets infected
Pustules: These are larger more inflamed papules filled with pus, skin cells and bacteria. They are red at the base and pus at the top
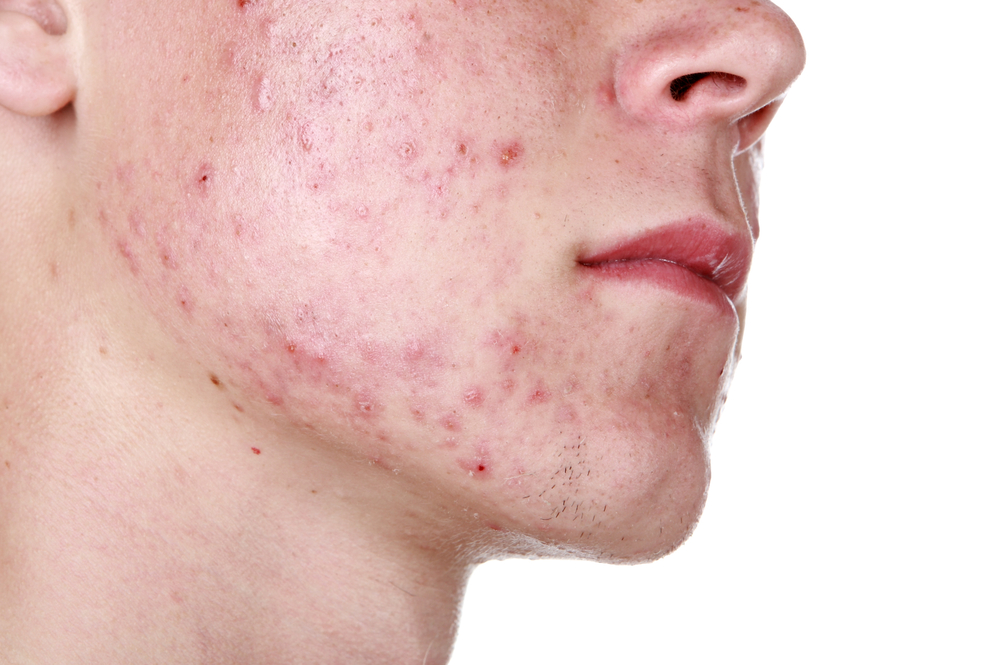
Nodules: A severe form of acne that presents as large, painful bumps under the skin and painful to touch. These can cause permanent scarring thus requires urgent medical attention.
Cysts: It is the worst form of acne and occurs when a severe inflammatory reaction results in boil-like fluid-filled nodules. Also requires urgent medical attention.
Back, Chest and Buttock Acne
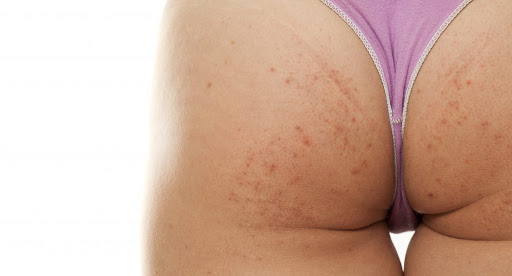
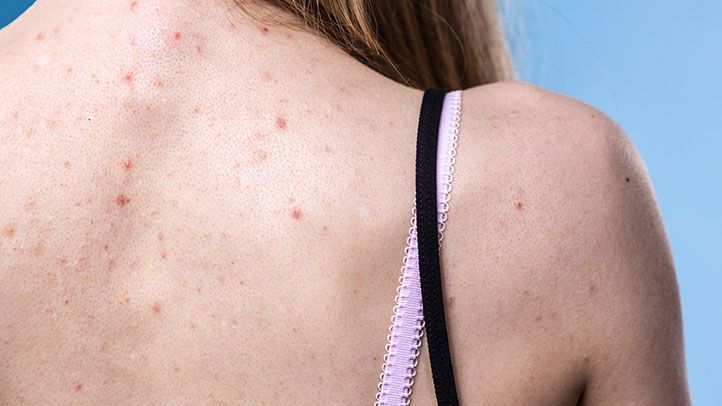
Affects most with acne-prone skin. It is unsightly with the area covered with spots and marks. The back and buttocks are difficult areas to treat with topicals as both larger areas to cover and areas difficult to reach. Recommended treatment for persistent back, chest and/or buttock acne is oral Isotretinoin. Benefits are no need for complicated applications of lotions and acne cleared usually stays cleared indefinitely. Chemical peels are effective to reduce and control acne as well as remove the marks at the same time.
The Causes Of Acne
The main cause is hormonal imbalance, mainly a rise in androgen levels. Increase in androgen levels causes oil glands under the skin to produce more sebum that both blocks up the pores, as well as cause inflammation and together with bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), causes infection…
Thus main factors in acne-prone skin are excess oil, blocked pores and hair follicles, infection.
Other possible causes:
Genetics
Emotional Stress
Medicine with hormones like the contraceptive pill and corticosteroids
Imbalance of hormones as in Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOs)
Greasy cosmetics
Does Diet Affect Acne?
Studies indicate that certain dietary factors such as dairy, carbohydrate-rich foods including chocolates can worsen acne. The recommended diet is one which has a low glycemic index and non-dairy. Encouraged to eat fruits and vegetables. Taking supplements with zinc has shown to help.
Complications of Acne
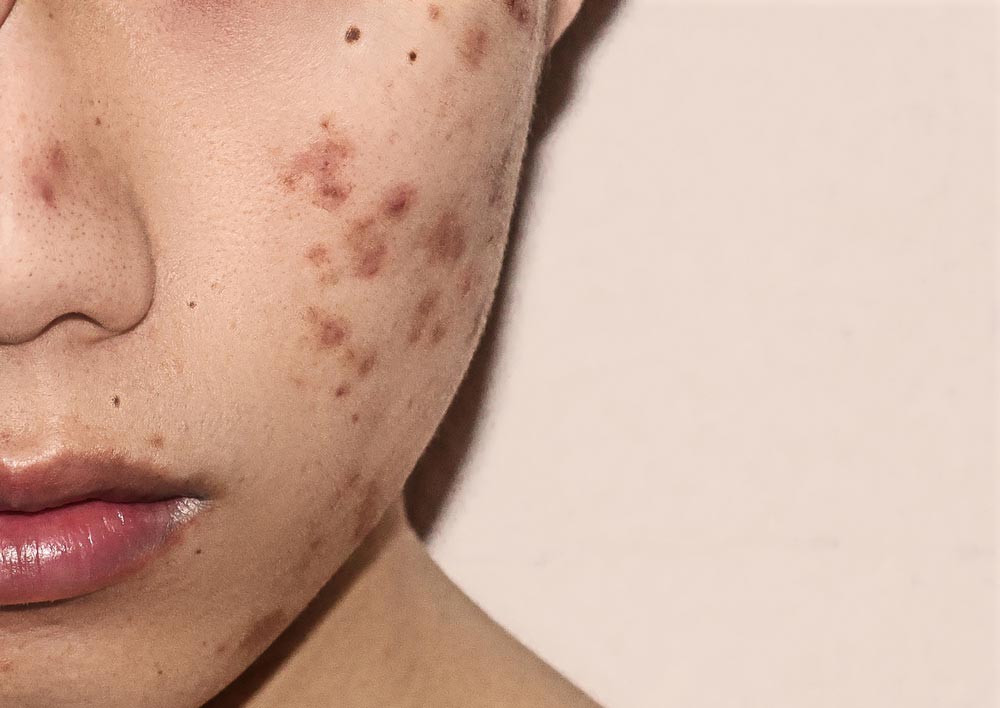
Acne scars
Acne is usually a temporary problem, unfortunately, acne scars can be permanent. Scars are part of the body’s natural healing process and usually occurs when acne affects deeper layers of the skin such as cystic or nodular acne. When the healing process is excessive it results in unsightly keloid scars. Read more
Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
These appear as dark spots on the skin and are termed as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. As the name suggests, it occurs after the inflammation of the pimple has subsided. These marks can be removed completely. Read more
Acne Scar Treatments
Mild Acne
Mild acne can be treated with over-the-counter products, but persistent or moderate to severe acne should be treated by a dermatologist. It is important that acne gets treated as soon as possible to minimise the number of scars on the face as scars are usually permanent. Treatment for scars can only improve the scars but not completely remove the scars.
1. Medicated Topicals
Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills bacteria and reduces sebum
Salicylic acid: Reduces inflammation and helps to remove blackheads and whiteheads
Retinoids: Topical retinoids such as tretinoin and adapalene are derivatives of vitamin A. Unblock pores through cell turnover and reduces sebum
Azelaic acid: Reduces bacterial growth and reduces sebum
Dalacin: Antibiotic used topically to reduce bacteria and inflammation. Topical antibiotics on its own is not a recommended acne treatment as they increase antibiotic resistance.
Topical acne treatment must comprise of at least 2 different types of topical medicated lotions so as to target most aspects of causes of acne, such as reducing illness, blockage of pores and hair follicles and infection.
Acne lotions and creams can be irritating and drying. Advisable to start gradually and to use a water-based moisturiser for the dryness.
2. Medical Facial
Medical Facials use microdermabrasion that both exfoliates to remove blackheads, whiteheads as well as infuse the skin with salicylic acid to further reduce acne. Medical facials complement acne treatments Read more
Moderate to Severe Acne
In such cases, in addition, medical treatments have to be added to acne creams/lotions
1. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are the most ideal treatment for acne as it not only clears up acne, it also removes marks and reduces acne scarring Read more
2. Blue Light Therapy
What is Blue Light Therapy?
Blue light therapy is a non-invasive FDA-approved treatment for acne vulgaris that is moderate or not responded to other treatments. It can be used in combination with other treatments. It uses a specific blue wavelength light to reduce the acne-causing bacteria and due to the anti-inflammatory effect, it reduces sebaceous gland size.
Blue light therapy is one of the few treatments that can be safely used to treat acne exacerbation during pregnancy
What to expect?
Painless treatment that lasts 10-15 minutes and requires 2 sessions a week for 4 weeks.
A safe and minimal reaction such as some redness which goes away after a few hours.
3. Corticosteroid Injection
Corticosteroid Injections are indicated for the treatment of large cystic or nodular acne lesions that usually takes weeks to heal or remain as lumps after healing. The cyst/nodule reduces in size after a few days after the injection.
Adverse effects such as dimpling or hypopigmentation at the site of injection can sometimes occur.
4. Oral Antibiotics
Given during acute phase. It is our policy not to have patients taking antibiotics for prolonged periods as it affects Gut health. Thus antibiotics are only prescribed for about 4-6 weeks only. Antibiotics become unnecessary after a month as the acne is usually successfully controlled by procedures implemented at the start of therapy.
5. Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin is an oral vitamin A and considered the most effective acne treatment that has the potential to clear up acne completely, especially for severe nodular/cystic acne and recurring acne that has not responded to any other treatments.
Such acne types leave permanent scars. Thus it is best to start early when such type of acne appears to minimise scars.
It is also recommended for acne that affects large areas of the body that includes face, chest and back or recurring back or buttock acne.
How does it work?
Isotretinoin works by shrinking the sebaceous glands that produce excess sebum in acne-prone skin. When skin stops producing excess oil, there is no more clogging of pores and creating pimples.
A blood test is done to determine liver function before isotretinoin is prescribed. A consent form has to be signed to indicate an understanding of no pregnancy during and 6 months after therapy ends.
Patients take 1-2 capsules a day for a period of 8-10 months depending on daily dose vs body weight.
It can take up to 4 months before no more new pimples appear. In some cases, there is a flare-up of acne in the first month and it can be controlled with oral antibiotics. After treatment is finished, pimples rarely return. Even if they do, it is usually mild.
What are the side effects?
Dry eyes, lips and nose
Nose bleeds
Photosensitivity
Not common side effects:
Nausea
Thinning of hair
Depression
Bone and joint
High blood triglycerides
Headaches
Severe Birth defects
6. Oral Contraceptive
Oral contraceptive such as DianeED is effective to control acne due to hormonal imbalance. Especially useful when acne is associated with menstrual irregularities
Do’s and Don’ts with Acne-Prone Skin
• Most important is if you are unable to manage acne with OTC products, come in for a consultation as soon as possible as the longer you leave it more scars there will be on the face. Scars are most difficult to treat compared to treating acne!
• Wash face at least twice a day using a specific cleanser for acne-prone skin
• Avoid popping pimples as likely to drive infection deeper into the skin making the infection worse and likely to leave scars
• Do not scrub face as will worsen acne
• Keep phone from the face when talking as phones are most contaminated.
• Keep hands off the face
• Avoid using facial products that are oil-based




